STE(A)M in Catalonia (Spain)

The Government of Catalonia, some universities and some jointly private initiatives are promoting STE(A)M education through different initiatives at Catalonia. Supporting teachers and learners, creating and developing activities and generating new communities are the main strategies developed.
In Spain, the educational competences of the formal levels of education are divided between the state government (Ministry of Education and Professional Training) and the regional governments (Councils or Departments of Education). In this way, the Ministry of Education and Vocational Training establishes the common contents and assessable learning standards of core subjects and sets the minimum number of hours for core subjects. The Departments for Education of the Autonomous Communities complement the contents of core subjects, and they establish the contents of specific subjects and the subjects that are freely structured by the Autonomous Communities. Accordingly, the regional government makes methodological recommendations to educational institutions within their remit.
Thus, everything that is related to formal education in the field of STE(A)M is the responsibility of regional governments. Let’s focus on Catalonia, where Colectic, the STEAMonEdu partner, is implementing this project.
First it was STEM, then it was STE(A)M. Public initiatives.
In 2009, the government established that the Catalan Department of Education should favor initiatives for the development of pedagogical and curricular innovation projects that aim to stimulate the capacity, learning, personal skills and potential of educators, the school success of all students, the improvement of educational activity, and the development of educational projects of the educational centers. It also stated that these projects may refer to one or more centers and involve, where appropriate, links with universities, economic sector or other organizations. The two decrees – Decree 119/2015 of 23 June on the organization of primary education and Decree 187/2015 of 25 August on the organization of compulsory secondary education – determined the competences in the scientific, technological and mathematical fields and their evaluation.
In 2016, in relation to the STEM disciplines (Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths), the Parliament of Catalonia urged the educational authorities to take the necessary actions to ensure that all students achieve, during primary education, the necessary basic skills to be, in addition to consumers, creators of technological solutions in the digital society, taking into account the digital competence that students must develop at this stage Therefore, the mandate implies that programming and educational robotics activities should be developed at school from of the first courses of compulsory education.
Subsequently, by Government Agreement on 2017, the STEMcat interdepartmental working group was created, with the aim of drawing up and monitoring a plan to promote scientific and technological vocations in engineering and mathematics with students in Catalonia (STEMcat), which includes, among its priority lines, the promotion of scientific, technological and mathematical skills among students in compulsory education.
SteamCAT and Bitbot: the government leadership
A big step was taken a little bit later: with the aim of promoting the scientific, technological, engineering and mathematical vocations through creativity, design and art in students in Catalonia, the STEAMcat pedagogical innovation programme was created in 2018 (see the official government document). The programme is part of the support for innovation and research, which is one of the lines of action in relation to the specific objectives mentioned, and which must also contribute to the overall improvement of the other actions of the STEMcat Plan.
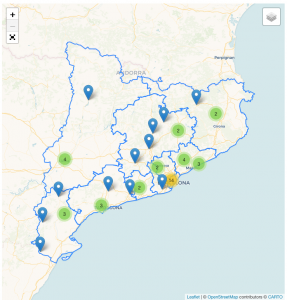
STEAMcat community of centers – Comunitat STEAMcat
The joint work of active, participatory and learning methodologies, the competence work of the contents of the different STEM disciplines and the regulatory evaluation of learning in the extension of the center, together with the educational orientation, must contribute to the promotion of STEM vocations and also to achieving the increase of these vocations among women. At first, 40 educational centers were selected (20 Infant and Primary Education centers and 20 Compulsory Secondary Education centers) to be part of the STEAMcat pedagogical innovation programme from the 2018-2019 academic year. Nowadays, 51 educational centers are part of the community.
In Catalonia, the formal network of STEAMcat educational centers emphasize the relevance of equity and promotion of the scientific-technological vocations among women and in disadvantaged social contexts.
The STEAMcat programme aims to boost the development of teachers’ professional skills and the application of methodologies that promote in students an improvement in the understanding of the world, based on scientific, technological, mathematical and engineering contents, from creativity, the arts and the humanist vision that critical thinking entails. (Source)
Their detailed objectives are to:
- Increase the scientific-technological and mathematical vocations especially in women and disadvantaged social contexts.
- Reinforce the process of orientation of the students towards the studies and professions of the field STEM in terms of equity and in all the educational stages.
- Improve the ability to understand and interpret a scientific-technological and mathematical world.
- Improve the social perception of STE(A)M areas.
- Improve the personal attitude towards the learning of the scientific-technical and mathematical areas, in the group of the students from the infantile education to baccalaureate.
- Increase the application of transversal learning methodologies, generators and vehicles of shared knowledge between the different scientific, technological, artistic and mathematical fields that encourage critical thinking and creativity.
- Promote the creation of alliances between the educational centers, the agents of the scientific-technological field and the near surroundings by means of the realization of activities related with socially relevant problems.
- Share research as teachers and reflective practice among members of the STEAMcat community.
Screenshot of the STEAMcat website
The STEAMcat pedagogical innovation programme consists of supporting the centers through advice, the creation of the STEAMcat Community, training and resources. Taking advantage of the distributed leadership of the educational centers, the methodologies, perspectives and technologies appropriate to the classroom and the transversal work of the teaching staff, the critical thinking of the students is encouraged, and the social perception of science is improved, to bring about an increase of the selection of post-compulsory STEM studies for a positive change in students’ self-perception towards these disciplines. (Source)
A complementary but really relevant action was taken by the Secretariat for Digital Policies, in collaboration with the Department of Education: creation and promotion of the Bitbot programme to increase the extracurricular offer of activities in the field of programming and educational robotics in Catalonia. This programme stimulate and promote the private initiative in order to achieve one goal: to have more STE(A)M activities in the after-schools programmes.
STE(A)M: universities and private initiatives
Some Universities have also created similar initiatives. For example, Aquí STEAM (Here STEAM) is an initiative of the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) specifically aimed at girls between 9 and 14 years old in Catalonia to attract female talent to study technology and engineering. The programme aims to break the stereotypes and gender roles established in society and to make visible new female references in an attractive and close way for girls.
Screenshot of the Aqui Steam website
Another great example is the new STEAM en acción (STEAM in Action) that will be developed by La Fundació Aigües de Manresa – Junta de la Sèquia, the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) and financed by the bank BBVA. It is a transversal educational proposal that aims to educate students from day-to-day experiences. In addition to one exhibition, “Mathematics and life”, multidisciplinary and interactive activities have been designed, aimed at an audience ranging from 3 to 18 years old, all of them thought and developed by UPC members.
Fundació Catalana per a la Recerca i la Innovació (Catalan Foundation for Research and Innovation,a private entity funded with public sources ) develop the Open STEAM teaching innovation workshops, offering support and updating to teachers for the introduction of the scientific method in primary, secondary and high school classrooms. Its content provides a practical approach to encourage teacher training in scientific experimentation activities, aimed at these educational levels.
At a national level, Inspira STEAM is a pioneer project for the promotion of the scientific-technological vocation among girls, based on awareness-raising and orientation actions taught by professional women from the world of research, science and technology. This is the first time that the group mentoring technique has been used in a project to promote STE(A)M (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts and Maths) among elementary school students. It is held by the Universidad de Deusto, with the cooperation of Innobasque in Euskadi, Edenway and the Universitat Rovira i Virgili in Catalonia, CIONET in Madrid, UCA and Universidad de Jaén in Andalusia, Universidad de Vigo and the Universidade da Coruña in Galicia, the Universidad de Oviedo in Asturias, the UCAM in Murcia and with the cooperation of companies as BBK, Roche, Barcelona Activa, Silk, HP Foundation among other companies. Tons of talent and a supra-territorial vision to make this initiative possible.

Screenshot of the Inspira STEAM website
Conclusions
The initiatives highlighted in this article, and some others that complement them, are promoted at different levels by private and public initiatives. In Catalonia, the STE(A)M is in the classrooms.
By Colectic
Featured image from Pixabay


